Page 265 - Hitachi IR 2025
P. 265
(d) Embedded foreign currency are measured similarly to the foreign currency forward contracts. The
embedded derivatives are foreign currency forward contracts which are separated from long-term
sales contracts and purchase contracts where the transaction currency differs from the functional
currencies of the involved parties. These contracts require physical delivery and will be held
for the purpose of the delivery of the commodity in accordance with the buyers’ expected sale
requirements. These contracts have embedded foreign exchange derivatives that are required to
be separated.
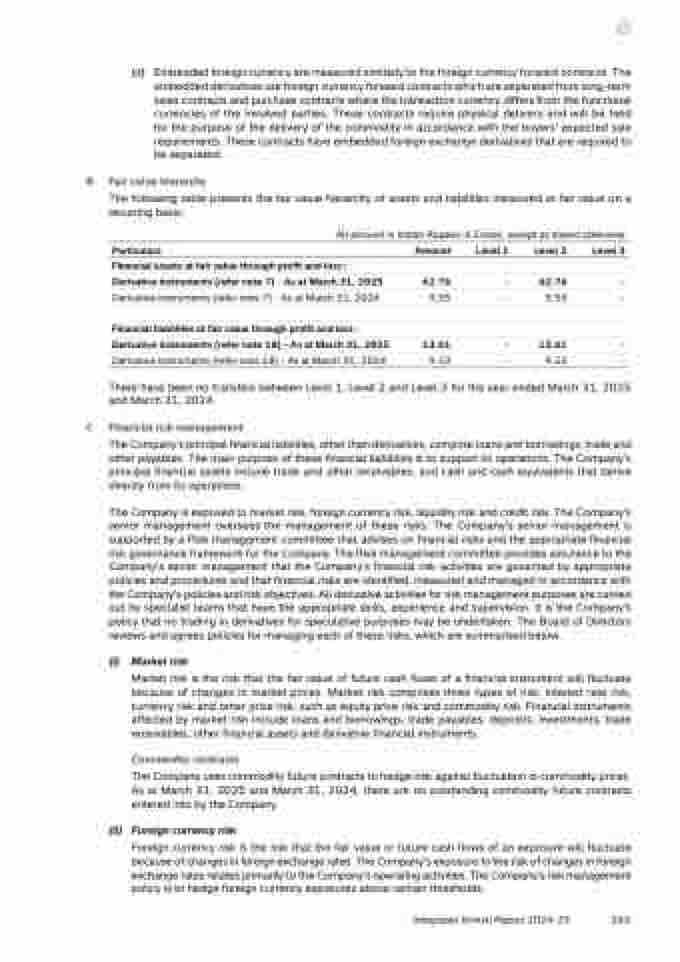
B Fair value hierarchy
recurring basis:
The following table presents the fair value hierarchy of assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a
All amount in Indian Rupees in Crores, except as stated otherwise
Particulars Amount Level 1 Level 2 Level 3
Financial assets at fair value through profit and loss :
Derivative instruments (refer note 7) - As at March 31, 2025 62.76 - 62.76 -
Derivative instruments (refer note 7) - As at March 31, 2024 9.55 - 9.55 -
Financial liabilities at fair value through profit and loss :
Derivative instruments (refer note 18) - As at March 31, 2025 13.61 - 13.61 -
Derivative instruments (refer note 18) - As at March 31, 2024 9.23 - 9.23 -
There have been no transfers between Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3 for the year ended March 31, 2025
and March 31, 2024.
C Financial risk management
The Company’s principal financial liabilities, other than derivatives, comprise loans and borrowings, trade and
other payables. The main purpose of these financial liabilities is to support its operations. The Company’s
principal financial assets include trade and other receivables, and cash and cash equivalents that derive
directly from its operations.
The Company is exposed to market risk, foreign currency risk, liquidity risk and credit risk. The Company’s
senior management oversees the management of these risks. The Company’s senior management is
supported by a Risk management committee that advises on financial risks and the appropriate financial
risk governance framework for the Company. The Risk management committee provides assurance to the
Company’s senior management that the Company’s financial risk activities are governed by appropriate
policies and procedures and that financial risks are identified, measured and managed in accordance with
the Company’s policies and risk objectives. All derivative activities for risk management purposes are carried
out by specialist teams that have the appropriate skills, experience and supervision. It is the Company’s
policy that no trading in derivatives for speculative purposes may be undertaken. The Board of Directors
reviews and agrees policies for managing each of these risks, which are summarised below.
(i) Market risk
Market risk is the risk that the fair value of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate
because of changes in market prices. Market risk comprises three types of risk: interest rate risk,
currency risk and other price risk, such as equity price risk and commodity risk. Financial instruments
affected by market risk include loans and borrowings, trade payables, deposits, investments, trade
receivables, other financial assets and derivative financial instruments.
Commodity contracts
The Company uses commodity future contracts to hedge risk against fluctuation in commodity prices.
As at March 31, 2025 and March 31, 2024, there are no outstanding commodity future contracts
entered into by the Company.
(ii) Foreign currency risk
Foreign currency risk is the risk that the fair value or future cash flows of an exposure will fluctuate
because of changes in foreign exchange rates. The Company’s exposure to the risk of changes in foreign
exchange rates relates primarily to the Company’s operating activities. The Company’s risk management
policy is to hedge foreign currency exposures above certain thresholds.
Integrated Annual Report 2024-25
263